Authorization server basics
The services of an authorization server, such as token service and introspection service, are usually protected. To obtain a token, the clients will need to authenticate themselves to the authorization server. Client authentication is a way for authorization servers to identify the client and either allow or prevent them from obtaining an access token.
Authorization servers support many ways of client authentication as listed below.
The preferred choice depends on a few factors, such as the security requirements of the organization and the client type (public or confidential). When registering an OAuth2.0 client with the authorization server, the client authentication method is specified, which defines the client_secret (aka the client password) and the method of including the secret in the request to the token service.
TLS for OAuth client authentication
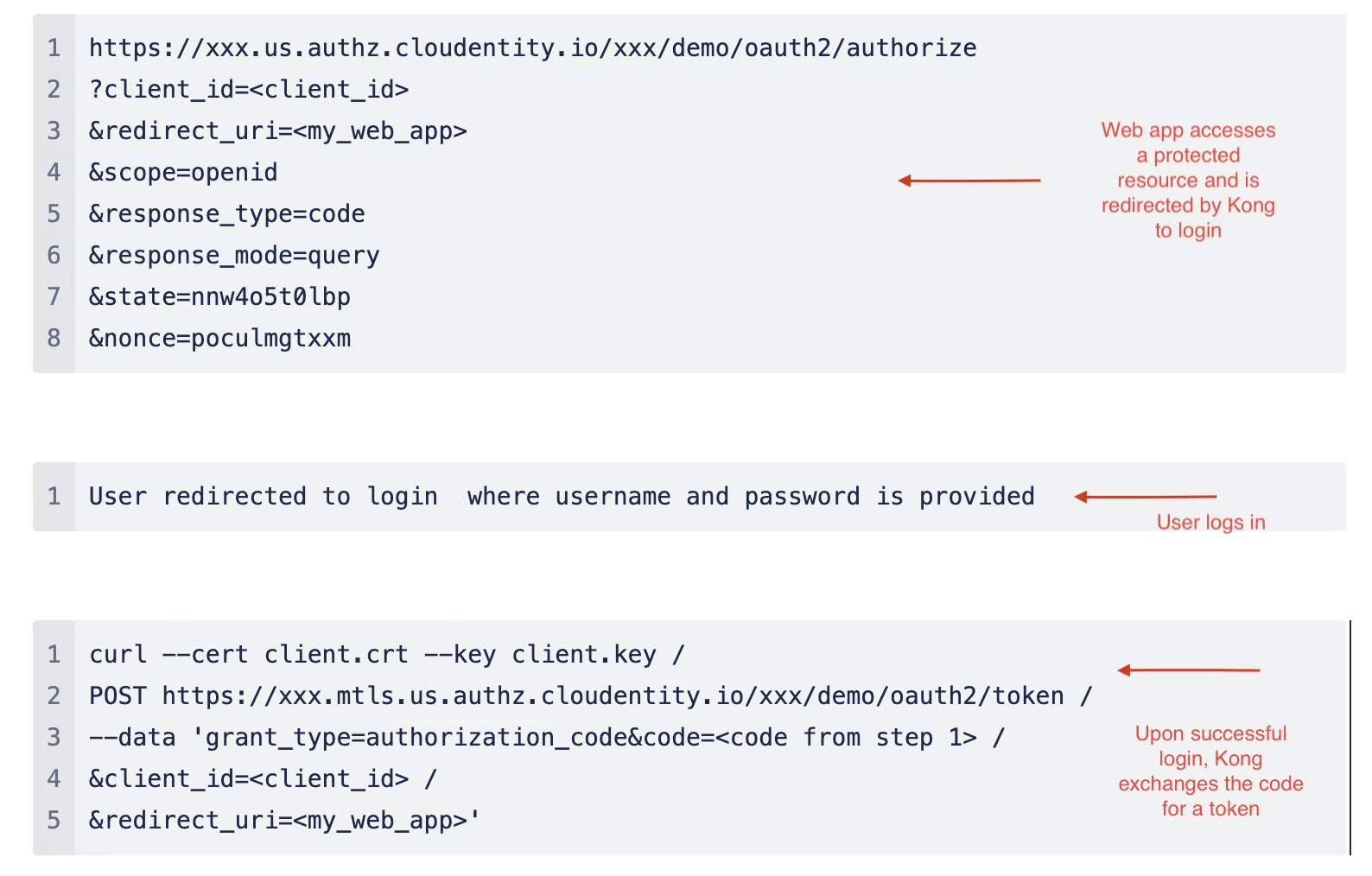
This method of client authentication uses X.509 client certificates as client credentials. Utilizing TLS certificates for client authentication provides better security characteristics than a shared secrets method. Mutual TLS (mTLS) is often used in this flow so that both the client and the authorization server can verify each other. mTLS is often used in a zero trust security framework. For environments with elevated security needs or those that need to adhere to zero trust principals, an mTLS-based solution becomes mandatory.
TLS client authentication support in Kong
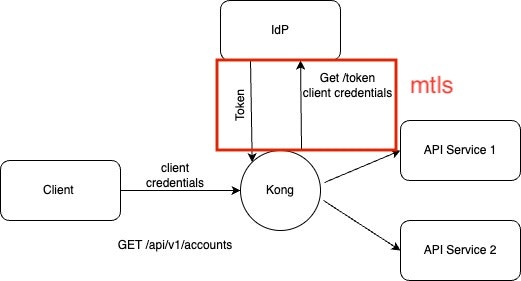
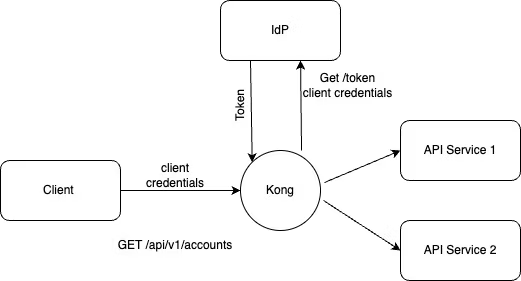
Kong supports all OAuth2.0 and OpenID connect (OIDC) flows via the OIDC plugin. With the Kong Gateway Enterprise 3.6 release, the OIDC plugin supports TLS Client Authentication as one of the authentication methods for the following endpoints in corresponding flows.
token
introspection
revocation
In the flows listed above, when the plugin is configured to use TLS Client Authentication, Kong establishes or reestablishes a mTLS connection to the authorization server (IdP) using the specified client certificate (figure 2). Kong also includes the client_id in all of the requests to the authorization server. The token is granted by the token service once the authorization server verifies Kong's certificate. Kong can also be configured to optionally verify the server certificate to achieve end-to-end mTLS.